Any type of drilling produces waste material and wastewater, and thus, water contamination has long been an area of research and mitigation in drilling applications. Geothermal can take advantage of this legacy of environmental focus by adapting and refining management practices from the oil and gas industry. Methods of water management and safe disposal are similar. Many lessons have been learned and best practices established that minimize the potential for inadvertent release, and that improve our understanding of the pathways leading to contamination of land, surface water, or groundwater.1Beard, J.C., and Jones, B.A., eds. (2023, May 1). Chapter 10: Environmental Considerations and Impact. The Future of Geothermal in Texas. p. 267. https://energy.utexas.edu/research/geothermal-texas
Common waste materials in the drilling process are bentonite, polymers, rock cuttings, and salts. Geothermal water will contain impurities such as dissolved solids, toxic H2S, and other corrosive gasses. Some of these impurities can be removed and used as a resource in other applications.2Beard, J.C., and Jones, B.A., eds. (2023, May 1). Chapter 10: Environmental Considerations and Impact. The Future of Geothermal in Texas. p. 267. https://energy.utexas.edu/research/geothermal-texas
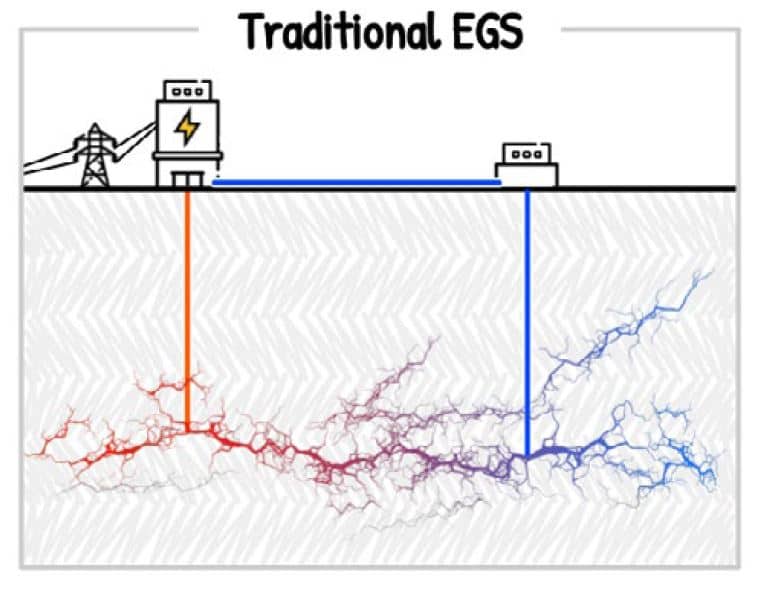
Because hydraulic fracturing techniques are used to enhance the geothermal reservoir, special attention to protecting our water resources through good injection-well design, use of high-integrity cement to prevent communication between the well and surrounding rocks, and avoidance or mitigation of surface spills is part of best management practices. In addition, natural proppant material (sand) used during hydraulic fracturing activities requires substantial excavation and, in some cases, water resources to mine and process the sand. Depending on the climate of the region and the number of wells to be stimulated, the volume of water could be significant.3Beard, J.C., and Jones, B.A., eds. (2023, May 1). Chapter 10: Environmental Considerations and Impact. The Future of Geothermal in Texas. p. 267. https://energy.utexas.edu/research/geothermal-texas
Would the use of sand as a proppant for hydraulic fracturing impact the environmental consideration for water use?
Correct
Incorrect
The oil and gas industry have a long history and large datasets to use to identify potential environmental impacts for the growing geothermal industry. As geothermal energy increases in Texas and the United States, we will have more specific geothermal project case studies to assist us in protecting our water resources.4Beard, J.C., and Jones, B.A., eds. (2023, May 1). Chapter 10: Environmental Considerations and Impact. The Future of Geothermal in Texas. p. 267. https://energy.utexas.edu/research/geothermal-texas
Image Credits
- Traditional-EGS-hydraulic-fracturing-FOGIT: The Future of Geothermal in Texas